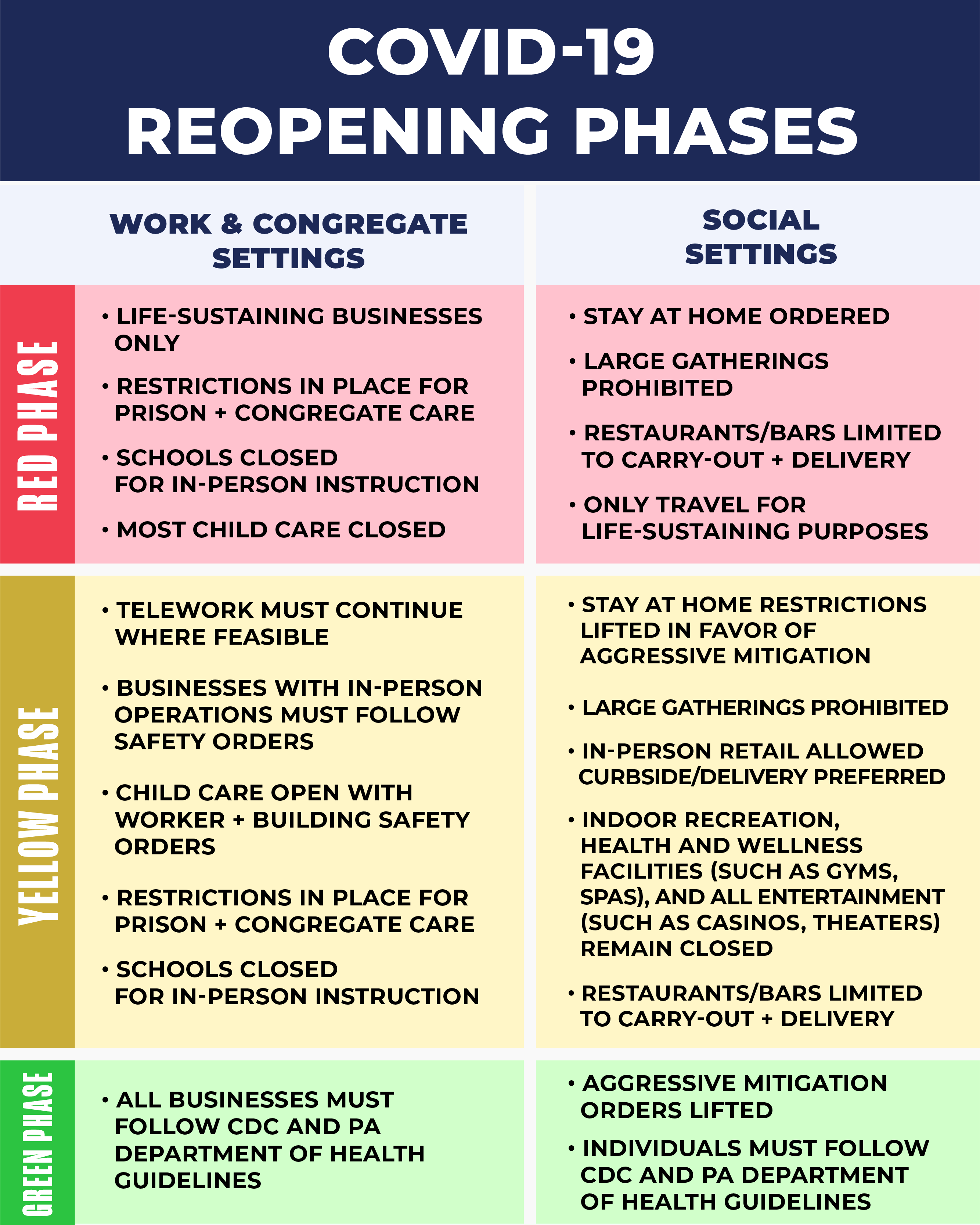
Media pundits and politicians are now in the habit of claiming it was the pandemic itself that has caused unemployment to skyrocket and economic growth to plummet. The claim is that sick and dying workers, fearful consumers, and disrupted supply chains would cause economic chaos. Some have even claimed that economic shutdowns actually help the economy, because it is claimed allowing the spread of the disease will itself destroy employment and economic growth.1
Leaving aside the fact there's no evidence lockdowns actually work, we can nonetheless look to past pandemics—where coercive government interventions were at most sporadic—we should see immense economic damage. Specifically, we can look to the the pandemic of 1957-58, which was more deadly than the COVID-19 pandemic has been so far. We can also look to the 1918-19 pandemic. Yet, we will see that neither produced economic damage on a scale we now see as a result of the government mandated lockdowns. This thoroughly undermines the claims that the lockdowns are only a minor factor in economic destruction, and that the virus itself is the real culprit.
Economic Reactions in 1957–58, and in 1918–19
The CDC estimates that as of May 18 this year approximately ninety thousand Americans have died of COVID-19. Adjusted for population size, that comes out to a mortality rate of 272 per million.
This is (so far) less than half the mortality rate for the 1957–58 flu pandemic. In that pandemic, it is estimated that as many as 116,000 Americans died. Yet, the US population was much smaller then, totaling only 175 million. Adjusted for population size, mortality as a result of the "Asian flu" pandemic of 1957–58 was more than 660 per million.
That's the equivalent of 220,000 deaths in the United States today.
Yet, Americans in 1957 did not respond by shutting down commerce, forcing people into "lockdown," or driving unemployment up to Depression-era levels. In fact, reports show that Americans took little action beyond the usual measures involved in trying to slow the spread of disease: hand washing, staying home when ill, etc.